Return in Python | Python Return Statement
A return in Python is a keyword that passes (or returns) a value or data from the function back to the main code.
When we declare a return keyword with a value or expression separating by the comma, then we call it a return statement. It is used to return a value from a function to the caller.
A function that returns some computed result in the terms of a value to the caller is called fruitful function or non-void function in Python.
A function that does not return any computed or final value to the caller is called void function. It may or may not have a return statement.
Syntax to Declare Return Statement in Python
The general syntax to declare a return statement inside a function is as:
def function_name(formal_parameters):
. . . . . . .
function's body
. . . . . . .
return <values/expression>
In the above function declaration, the first line is function header, and the rest is the function’s body. The function header starts with a keyword def followed by the function name, then an optional formal parameter list and a character colon (:).
Optional formal parameter list contains variable named separated by commas. The header must end with a colon. All the codes inside the body of function must be intended.
At the end, the return statement which is an optional. The return statement ends the execution of function call and returns the result, i.e. the value of expression following return keyword, to the caller function.
Function Call Statement Syntax:
var_name = function_name(arguement_list)
In the above function call statement, argument_list is the actual parameters or argument values that we send them to the function’s formal parameters during function call.
Key Points of Python Return Statement
There are a few key points about the return statement that you should keep in mind. They are:
1. Return statement finishes the function call’s execution and returns the result (value or expression).
2. Python function can have one or more return statement but only one statement will execute based on the matching condition.
3. A void function may or may not return a value to the caller. If the function does not contain a return statement, it will send a None value that represents nothingness. Consider the following function code below:
Example 1:
def greet(name): # Function without return statement.
"""Greets the person
passed as argument"""
print('Hello ' + name + ', Good Morning!')
print(greet('Mark'))
Output:
Hello Mark, Good Morning!
None
In this example, the greet() function does not return explicitly a value. It simply prints a message on the console. Since the function does not have a return keyword, it prints None value, which is implicitly sent by functions without return statement.
4. A function that returns a value, always have a caller which call and receives the final value of a function.
5. Return None is the same as a return statement with no argument value or expression. This means that a void function has a return statement, but it is not returning any value to the caller. It has the following general syntax.
return6. A return statement may return more than one value from the function to the caller. It has the following general syntax.
return <value1>, <value2>, <value3>, . . . .
7. The statement following the return statement will not execute. For example:
def dispMessage(msg): # Void function with return statement.
print(msg)
return # returning not value.
print('Programming')
print(dispMessage('I love Python'))
Output:
I love Python
None
8. We cannot use the return statement in the Python function.
Example Program based on Function Returning a Value
Example 1:
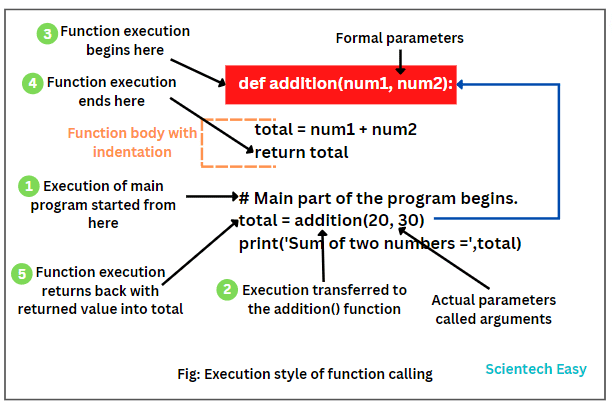
Let’s write a simple program in Python that will return the sum of two numbers to the caller.
# Function with return statement.
def addition(num1, num2):
total = num1 + num2
return total # returning a single value from a function.
# Main part of program execution starts here.
total = addition(20, 30) # Calling function with passing two values.
print('Sum of two numbers =',total)
Output:
Sum of two numbers = 50
In this example, we have defined a function named addition that has two parameters num1 and num2. When we have called this function with passing two argument values 20 and 30, it calculates the sum of two numbers and returned that values to the caller.
Then, we have stored the returned value into a variable named total and printed it on the console. Look the complete execution style of function addition in the below figure.
Example 2:
Let’s write a simple program in Python to calculate the cube of a number. We will take a number from the user.
def calCube(x):
return x * x * x # x is the formal parameter.
def main_function():
n = int(input('Enter your number: '))
# Calling function from another function.
result = calCube(n) # n is the actual parameter
print('Cube of a number = ',result)
# Calling main function.
main_function()
Output:
Enter your number: 5
Cube of a number = 125
Inside the main_function(), we have taken a number from the user using input() function, converted it into int and stored in a variable n.
Then, we have called the calCube() function with passing the value of n to the function’s parameter x. After the calculation of cube, function returned the value to the caller. We have assigned it into a variable result and then printed the result on the console.
Example 3:
Let’s write a program in Python to compute the area and circumference of circle using function and return statement.
PI = 3.14
def areaCircle(r):
area = PI * r * r
return area
def circumCircle(r):
circumference = 2 * PI * r
return circumference
def main_func():
radius = int(input('Enter radius of the circle: '))
area = areaCircle(radius)
circum = circumCircle(radius)
print('Area of circle =',area)
print('Circumference of circle =',circum)
main_func() # calling main function.
Output:
Enter radius of the circle: 3
Area of circle = 28.259999999999998
Circumference of circle = 18.84
Example 4:
Let’s write a Python program to make a simple calculator using function and return statement.
def add(x, y):
return x + y
def sub(a, b):
return a - b
def mult(p, q):
return p * q
def div(r, s):
return r / s
# Main program execution starts here.
def main_func():
n1 = int(input('Enter your first number: '))
n2 = int(input('Enter your second number: '))
# Calling functions.
print('Addition =',add(n1, n2))
print('Subtraction =',sub(n1, n2))
print('Multiplication =',mult(n1, n2))
print('Division =',div(n1, n2))
main_func() # calling main function.
Output:
Enter your first number: 10
Enter your second number: 5
Addition = 15
Subtraction = 5
Multiplication = 50
Division = 2.0
Python Function Return Multiple Values
We can return multiple values from a Python function. We separate the values after the return keyword by comma. Let’s take an example program based on it.
Example 1:
# Program to return multiple values from a function.
def func():
return 10, 'Hello', 'P', 20 # returning more than one value from a function.
p, q, r, s = func()
print(p)
print(q)
print(r)
print(s)
print(func())
Output:
10
Hello
P
20
(10, 'Hello', 'P', 20)
As you observe in the output, it seems that function can return more than one value. In fact, function returns a tuple.
Example 2:
Let’s write a program in Python in which we will take marks of five subjects from the student as a user. Then, we will calculate total marks and percentage of a student’s marks using function and return more than one value from a function. Look at the code below.
# Python program to return more than one value from a function.
def marks(m1, m2, m3, m4, m5):
total_marks = m1 + m2 + m3 + m4 + m5
percentage = total_marks / 5
# Returning more than one value from a function
return total_marks, percentage
# Main part of program.
def main_func():
m1 = int(input('Enter your Science marks: '))
m2 = int(input('Enter your Maths marks: '))
m3 = int(input('Enter your English marks: '))
m4 = int(input('Enter your Computer marks: '))
m5 = int(input('Enter your Hindi marks: '))
totalMarks, per = marks(m1, m2, m3, m4, m5)
print('Total marks obtained = ',totalMarks)
print('Percentage =',per)
main_func() # calling main function.
Output:
Enter your Science marks: 75
Enter your Maths marks: 85
Enter your English marks: 72
Enter your Computer marks: 65
Enter your Hindi marks: 72
Total marks obtained = 369
Percentage = 73.8
In this tutorial, you have learned about the return statement in Python with example programs. I hope that you will have understood how to return a value or more than one value from a Python function to the caller. Stay tuned with the next tutorial where you will know about void function in Python with examples.
Thanks for reading!!!