Accessing List Elements in Python
In Python, a list can have any number of elements or items. Just like strings, we can access each element of a list using list name, which is followed by a number in the unique index operator ([ ]) that specifies the position of an element in the list.
Each element in the list has a unique index that indicates its position or location. The syntax for accessing elements of a list is similar to the syntax for accessing characters of a string.
The general syntax to access an element of a list is as:
list_name[index]Here, the parameter index represents the position of an element in the list. It should always be an integer value to avoid TypeError. Attempting to access an element of list that is beyond the index range will outcome to an IndexError.
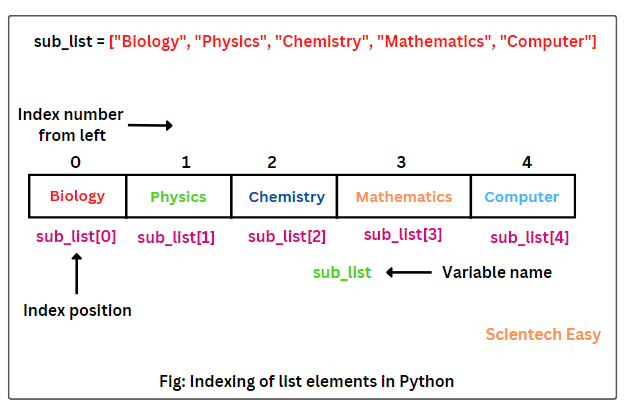
Python indexes elements in the list either from left to right or right end to left. When Python indexes list elements from left to right, the index of the first element is 0, index of the second element is 1, index of third element is 1, and so on.
Thus, elements of a list will gets allocated in the memory, as shown in the below figure.
From the above figure, the list sub_list contains five elements. The first element “Biology” of the list sub_list locates at index 0, the second element “Physics” locates at index 1, and so on.
Examples based on Accessing List Elements in Python
Example 1:
# Python program to access five elements of a list.
# Create a list.
sub_list = ["Biology", "Physics", "Chemistry", "Mathematics", "Computer"]
print("First element at index 0 is", sub_list[0])
print("Second element at index 1 is", sub_list[1])
print("Third element at index 2 is", sub_list[2])
print("Fourth element at index 3 is", sub_list[3])
print("Fifth element at index 4 is", sub_list[4])
Output:
First element at index 0 is Biology
Second element at index 1 is Physics
Third element at index 2 is Chemistry
Fourth element at index 3 is Mathematics
Fifth element at index 4 is Computer
In this example program, we have created a list of five elements and assigned it to a variable named sub_list. Then, we have accessed each list element by specifying the list name followed by a positive integer number (i.e. index value) in the square bracket ([ ]).
Example 2:
sub_list = ["Biology", "Physics", "Chemistry", "Mathematics", "Computer"]
print(sub_list[5])
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Python Project\AccessElements.py", line 3, in
print(sub_list[5])
IndexError: list index out of range
In this example program, we have attempted to access an element at an index that is not present on the list. Therefore, Python interpreter generates an error message.
Example 3:
# Python program to access characters of five elements of a list.
st_list = ["Bob", "Mark", "Deepak", "Harry", "Ivaan"]
print(st_list[0][1])
print(st_list[1][1])
print(st_list[2][3])
print(st_list[3][0])
print(st_list[4][4])
Output:
o
a
p
H
n
Accessing Nested List Elements in Python
In order to access the nested list, we will use nested indexing. Let’s take an example of it to understand better.
Example 4:
# Python program to access elements of a nested list.
nested_list = ["Code", 25, [1, 2, 3, 4], 25.5]
print(nested_list[0])
print(nested_list[0][2])
print(nested_list[1])
print(nested_list[2])
print(nested_list[2][1])
print(nested_list[2][3])
print(nested_list[3])
Output:
Code
d
25
[1, 2, 3, 4]
2
4
25.5
Access List Element using Negative Indexing
Python also supports to index elements of a list from right end to left. When Python indexes list elements from right end to left, it uses negative indexing. Look at the below figure.
The last element on the list takes -1 index, the second element from the last is -2 index, the third element from to the last is -3 index, and so on.
Example 5:
# Python program to access elements of a list using negative indexing.
char_list = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
print(char_list[-1])
print(char_list[-2])
print(char_list[-3])
print(char_list[-4])
print(char_list[-5])
Output:
e
d
c
b
a
In this tutorial, you have learned about how to access a list element in Python with example programs. Hope that you will have understood the basic concepts of accessing list and practiced all example programs.
Thanks for reading!!!