Substring in Python
Substring in Python is a subset of the main string specified by a range of indices. It is also a sequence of characters that is a portion of a given string.
Basically, substring is a extracting part of a string. For example, “Computer” is the substring for the string “Computer Science”.
We can extract a chunk of characters (called substring) from the original string with the help of slice syntax.
A slice syntax is a handy way to extract a substring from the original string. The general syntax for string slicing is as follows:
string_object[start:stop[:step]]
In the above syntax,
- start: It is a starting index where the slicing of string object begins. Its default value is 0.
- stop: It is a stopping index where slicing of string object ends. However, it is not included. Both start and stop indices in square brackets should be an integer value.
- step: It is an integer value that specifies the increment between each index for slicing. It basically refers to the number of characters that we can skip after start indexing character in the string. It is an optional parameter.
- colon: It specifies the range of value. It also separates the two indices in the square brackets ([ ]).
This slice syntax returns a substring beginning at the start index and extending up to but not including the stop index. The start and stop values should be an integer.
Python Substring Example Program
Let’s write a simple program to extract a substring within a string by specifying a range of index numbers separated by a colon.
Example 1:
# Program to demonstrate the extracting of substring from main string in Python.
# Original string.
str = 'Technology'
my_substring = str[0:4] # extracting substring by specifying a range of index numbers.
print("Substring:",my_substring)
Output:
Substring: Tech
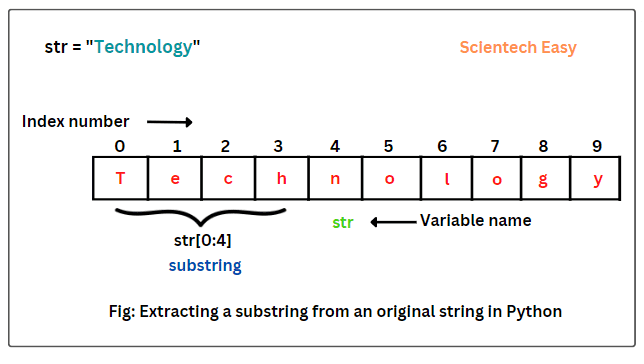
In the above code, we have created a variable named str and assign it with a string value “Technology”. The sequence of characters of this string will be index, starting from 0, and so on, as shown in the below figure.
We have obtained a substring of four characters starting from 0 to 4. The square brackets ([ ]) is a subscript operator. The first index number in the slicing operation represents the position from where the slice starts and the second index number after the colon indicates where slice will end.
Thus, the first index number is inclusive and the last index number is exclusive. Hence, 0:4 means 0 to 3 sequence of characters, not 4th character.
Example 2:
# Original string.
str = 'Good Morning'
print("Original string:",str)
# This statement starts to slice string at index 0 and slices up to index 4 and returns the result.
substring1 = str[0:4]
print('Substring from 0 to 4:',substring1)
# This statement starts to slice string from the beginning and slices up to index 6 and returns the result.
substring2 = str[:6]
print('Substring up to 6:',substring2)
# This statement starts string slicing at index 5 and slices up to end.
substring3 = str[5:]
print('Substring up to end:',substring3)
# This statement does not slice the string and displays the entire string.
substring4 = str[:]
print('Entire substring:',substring4)
# This statement produces an empty string.
substring5 = str[4:4]
print('Empty string:',substring5)
# This statement starts to slice the string at index 5 and slices up to end position (including).
substring6 = str[5:12]
print('Substring up to end:',substring6)
Output:
Original string: Good Morning
Substring from 0 to 4: Good
Substring up to 6: Good M
Substring up to end: Morning
Entire substring: Good Morning
Empty string:
Substring up to end: Morning
In this example program, we have defined a variable named str and assigned a string value “Good Morning” to it. Remember the following points while extracting substring from the original string using subscript operator. They are:
(a) The first number before the colon in the slicing operation indicates the position from where the slice begins.
(b) The second number after the colon in the slicing operation indicates where the slice will stop.
(c) If we do not specify the first number, Python will start to slice the sequence of characters from the beginning.
(d) If we do not specify the second number after the colon, Python will stop the slicing at the end of the sequence.
(e) Omitting both indices, Python extracts the entire string starting from 0 till the last index. That is, it returns a substring as a copy of whole string.
(f) If the first index is greater than or equal to second index, Python gives an empty string.
Creating Substring using Negative Index
We can also extract a sequence of characters from a string using negative index value. A negative index number begins from -1 from end of a string that represents the last character of the string.
The index decreases by one as we move from right to left. For example, -2 represents the second last character and so on.
While using negative index, specify the lowest negative integer number in the start index position. Let’s see an example program based on it.
Example 3:
# Original string.
str = 'Good Evening'
print("Original string:",str)
substring1 = str[-13:-8]
print("Substring:",substring1)
substring2 = str[-7:-1] # Here, last character positioned at -1 will be excluded.
print("Substring:",substring2)
Output:
Original string: Good Evening
Substring: Good
Substring: Evenin
Extracting Substring in Python using slice() Function
Python provides a built-in function named slice() that we can use to obtain substring from a string. This function returns a slice object we can use to slice a string.
Python language provides two overloaded slice() functions. The first function takes a single formal parameter ‘stop’ index, while the second function takes three formal parameters ‘start’ index, ‘stop’ index, and ‘step’ value as well.
The general syntax for slice() function with parameters is as:
slice(stop)
slice(start, stop, step)
Parameters:
(a) The first parameter “start” specifies the starting index at which the slicing of string object begins.
(b) The second parameter “stop” specifies the ending index where a string object’s slicing comes to a halt. The slice() function excludes the stop index while generating the substring. That is, the slice() doesn’t stop ‘at’ or ‘after’ the stop index. It stops just before this index when performing slicing.
(c) The third parameter “step” is an optional parameter that specifies the increment between each index for slicing. It basically refers to the number of characters that we can skip after start indexing character in the string.
If you pass only one parameter, start and stop parameters are considered to be None.
Let’s write a program in Python to extract substring from an original string using slice() function.
Example 4:
# Original string.
str = 'Scientech Easy'
print("Original string:",str)
substring1 = slice(5)
print("Substring:",str[substring1])
substring2 = slice(5, 9)
print("Substring:",str[substring2])
Output:
Original string: Scientech Easy
Substring: Scien
Substring: tech
In the above code,
(a) First, we have called the slice() function by passing an argument 5 to the ‘stop’ parameter. The slice() starts the slice object at position 0 and slice up to position 5 and returns the result as “Scien”. It automatically sets the ‘start’ index to 0. We have stored the returned result in a variable named substring1.
(b) Then, we have called slice() function by passing argument values 5 and 9 of ‘start’ and ‘stop’ indices, respectively. The slice() function creates a slice() object containing a substring from the position 5 up to the position 9 and returns the result as “tech”. We have stored the returned result in a variable substring2 and printed it on the console.
In this tutorial, you have learned about how to extract a substring from a given string in Python with the help of examples. Hope that you will have understood the basic concepts of extracting substring and practiced all example programs.
Thanks for reading!!!