When Finally Block Is Not Executed in Java
In this tutorial, we will familiar with some specific conditions in which finally block will not get executed in Java. So far, we have learned that a finally block always gets executed, whether we have handled exception in catch block thrown by corresponding try block or not.
The finally block will also get executed if a try block exists by using return, break, or continue statements. Let’s understand what are conditions in which the finally block is not executed in Java.
Condition where Finally Block is not executed in Java
In Java, there is one possibility where finally block will not be executed. They are as follows:
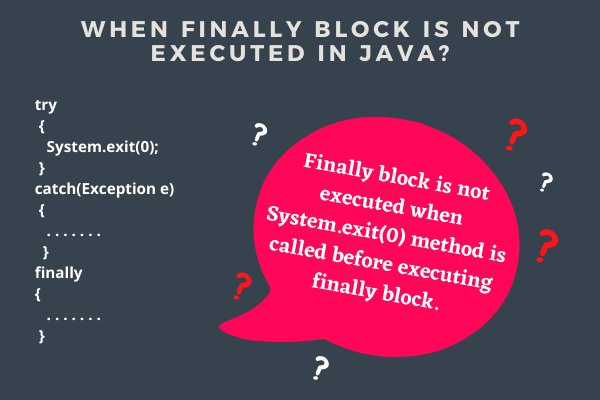
1. When the System.exit() method is called in the try block before the execution of finally block, finally block will not be executed.
Let’s take the different example programs based on the above condition.
Example 1:
package finallyProgram;
public class FinallyBlock1
{
void m1()
{
try {
System.out.println("I am in try block");
System.exit(0);
}
finally {
System.out.println("I am in finally block");
}
System.out.println("Statement after finally block");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FinallyBlock1 obj = new FinallyBlock1();
obj.m1();
}
}Output:
I am in try blockAs you can see in the preceding program code, when System.exist(0) method is called in try block, finally block and statement after finally block are not executed.
Example 2:
package finallyProgram;
public class FinallyBlock2 {
void m1()
{
int a = 20, b = 0;
try {
System.out.println("I am in try block");
System.exit(0);
int c = a/b;
System.out.println("Result: " +c);
}
catch(ArithmeticException ae)
{
System.out.println("I am in catch block");
}
finally {
System.out.println("I am in finally block");
}
System.out.println("Statement after finally block");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FinallyBlock2 obj = new FinallyBlock2();
obj.m1();
}
}Output:
I am in try blockExample 3:
package finallyProgram;
public class FinallyBlock3 {
void m1()
{
int a = 20, b = 0;
try {
System.out.println("I am in try block");
int c = a/b;
System.exit(0);
System.out.println("Result: " +c);
}
catch(ArithmeticException ae)
{
System.out.println("I am in catch block");
}
finally
{
System.out.println("I am in finally block");
}
System.out.println("Statement after finally block");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FinallyBlock3 obj = new FinallyBlock3();
obj.m1();
}
}Output:
I am in try block
I am in catch block
I am in finally block
Statement after finally blockConditions when statements in Finally Block are not executed in Java
There are two conditions in which statements in the finally block will not be executed in Java. They are as follows:
1. When the return statement is defined in the finally block, the control of execution is transferred to calling routine, and statements after the return statement in finally block are not executed.
2. When an exception occurs in the code written in the finally block. In this case, finally block does not complete normally.
Let’s take different kinds of example programs based on the above two conditions.
Example 4:
package finallyProgram;
public class FinallyBlock4 {
int m1()
{
int a = 20, b = 0;
try {
System.out.println("I am in try block");
int c = a/b;
System.exit(0);
System.out.println("Result: " +c);
}
catch(ArithmeticException ae)
{
System.out.println("I am in catch block");
return 20;
}
finally
{
System.out.println("I am in finally block");
return 50;
System.out.println("Statement after return statement"); // Unreachable code.
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FinallyBlock4 obj = new FinallyBlock4();
System.out.println(obj.m1());
}
}Output:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem:
Unreachable codeAs you can see in the above example program, statement after return statement in the finally block is not executed and Java compiler generates Unresolved compilation problem: “Unreachable code“.
Example 5:
package finallyProgram;
public class FinallyBlock5 {
int m1()
{
int a = 20, b = 0;
try
{
System.out.println("I am in try block");
int c = a/b;
System.exit(0);
System.out.println("Result: " +c);
}
catch(ArithmeticException ae)
{
System.out.println("I am in catch block");
return 20;
}
finally
{
System.out.println("I am in finally block");
return 50;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FinallyBlock5 obj = new FinallyBlock5();
System.out.println(obj.m1());
}
}Output:
I am in try block
I am in catch block
I am in finally block
50Example 6:
package finallyProgram;
public class FinallyBlock6 {
int m1()
{
int a = 20, b = 0;
try {
System.out.println("I am in try block");
int c = a/b;
System.out.println("Result: " +c);
}
catch(ArithmeticException ae)
{
System.out.println("I am in catch block");
System.exit(0);
return 20;
}
finally
{
System.out.println("I am in finally block");
return 50;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FinallyBlock6 obj = new FinallyBlock6();
System.out.println(obj.m1());
}
}Output:
I am in try block
I am in catch blockExample 7:
package finallyProgram;
public class FinallyBlock7 {
void m1()
{
int a = 20, b = 0;
try {
System.out.println("I am in try block");
int c = a/b;
System.out.println("Result: " +c);
}
catch(ArithmeticException ae)
{
System.out.println("I am in catch block");
}
finally
{
System.out.println("I am in finally block");
int x = 30/0; // Exception occurred in finally block.
System.out.println("Result: " +x);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
FinallyBlock7 obj = new FinallyBlock7();
obj.m1();
}
}Output:
I am in try block
Exception in thread "main" I am in catch block
I am in finally block
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at finallyProgram.FinallyBlock7.m1(FinallyBlock7.java:19)
at finallyProgram.FinallyBlock7.main(FinallyBlock7.java:26)
I hope that this tutorial has covered all types of example programs based on topic “when finally block is not executed”. All these programs are very important for the interview. So, practice wholeheartedly.
Thanks for reading!!!