What is Motherboard: Definition, Types
If you open your computer, you will see a large circuit board on the bottom or side of a computer case into which other circuit boards are plugged. This large circuit board is called motherboard.
Definition of Motherboard
A motherboard in a computer is a large rectangular circuit board that sits inside a computer case and controls the operations of all other components.
Sometimes, it is also known as a main board or system board. It is the main hardware component in any computer system that holds and connects together various essential components of a computer.
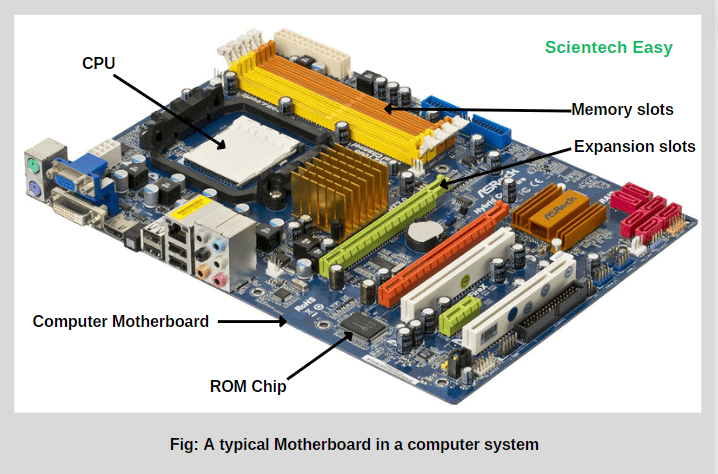
A computer motherboard usually accommodates a central processing unit (CPU), BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) memory chip, heat sink/fan assembly, RAM, expansion slots, chipset, sockets, internal and external connectors, and various ports. This board also contains embedded wires that interconnect motherboard components.
Why It is Called a Motherboard?
All the other circuit boards having chips or other electronic components are connected to a common circuit board called motherboard. Therefore, it is known as a mother of all other circuit boards.
A motherboard is a heart of any computer machine because it performs several important functions to the functioning of a computer. It provides electrical pathways and data transfer capabilities between the processor, memory, storage, expansion cards, and other peripheral devices.
Structure and Design of a Typical Motherboard
A typical computer motherboard consists of chipsets, multiple slots, connectors, and sockets designed to accommodate specific hardware, as shown in the below figure.
For example, CPU sockets allow the installation of one or more processors, memory slots hold RAM modules, and expansion slots enable for the addition of expansion cards (such as graphics cards, sound cards, or network cards).
This main circuit board provides a common platform through which all the hardware components of a computer system communicate or interact with each other and perform necessary functions. The computer’s overall performance and functionality may be significantly impacted by its design, compatibility, and capabilities.
Computer Motherboard: A Brief History
There are three basic factors that generally affect all the computer motherboards. They are:
- Form Factor: It determines the actual physical dimensions, layout, and mounting style of of the board.
- Chipset: It specifies what supporting chips will place on the board to control the flow of data between CPU, memory, and peripherals.
- Bus: It defined the actual design of the circuit traces on the board and the electrical signals that flow across the circuit traces.
The Beginning (1981 – IBM Planar Board)
In Aug 1981, IBM (International Business Machines Corporation) had introduced the first motherboard named “planar board” in the world. It had installed in the original IBM personal computer (PC) to provide the basic of computing to the home user.
This PC’s motherboard had included an Intel processor chip, and 16 kilobytes of memory chip (expandable to 256 kilobytes). It had five expansion slots that were configured much like today’s ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) slots.
The bus structure could handle only 8 bits of information at a time. The back of the circuit board has two connectors, one for the connection of a keyboard, and second for the connection of a cassette tap.
IBM XT Motherboard (1983)
In 1983, IBM released eXtended Technology (XT) computer with three additional expansion slots added to the motherboard. However, keyboard connectors became standard on all the later motherboards, and floppy drives replaced the cassette connector. The capability of primary memory RAM was increased to 640 KB. IBM introduced the first internal hard drives, making a major step forward in PC technology.
IBM AT Motherboard (1984)
In 1984, IBM released the Advanced Technology (AT) motherboard, a major advancement over the earlier designs. This technology made the PC better than the previous. The AT form factor used a 16-bit data bus (paths), meaning that it allows to travel 16 bits of information across the motherboard at a time.
The ISA slots were converted to 16-bit slots. However, one or two slots had kept to an 8-bit configuration for backward compatibility with XT boards. The AT motherboard design became the standard architecture for PCs throughout the 1980s and influenced future motherboard formats such as Baby AT and ATX.
Other Form Factors
After IBM’s AT motherboard, several other form factors were developed over time to improve efficiency, size, and compatibility:
- Baby AT (1985): This is a smaller version of the AT motherboard, which was widely used until the mid-1990s.
- ATX (1995): This is introduced by Intel, which became the most popular motherboard form factor. It offered improved power management, better component placement, and enhanced airflow.
- MicroATX, Mini-ITX, and others: Later innovations that focused on compact designs for modern desktop and small form factor computers.
Types of Motherboard in Computer
Motherboards of a computer come in different sizes (form factors), shapes, and features depending on their purpose and compatibility. Here are its major types of computer motherboards:
- eXtended Technology (XT)
- Advanced Technology (AT)
- Standard ATX
- Micro ATX
- Mini-ITX
- Mini STX
- Extended ATX (EATX)
Modern Motherboard Types
- Nano-ITX
- Pico-ITX
- Thin Mini-ITX
Let us understand each type of motherboard and its characteristics in brief.
XT Motherboard
In March, 1983, IBM introduced XT (eXtended Technology) motherboard, which was used to upgrade the original IBM Personal Computer (XT) model. It played a significant role in the early development of personal computing.
- Form Factor: The XT motherboard had a rectangular shape and measured approximately 8.5 x 11 inches (216 x 279 mm). This form factor became the standard for early desktop computers in the 1980s.
- Processor Support: On this motherboard, there was a processor socket to accommodate 8-bit Intel 8088 processor, enabling data transfer and control between various components of the system.
- Expansion Slots: The XT motherboard typically had 5 to 8 ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) expansion slots, memory slots, a BIOS chip, and various connectors. The expansion slots allowed the users to install additional expansion cards, such as graphics, sound, and networking cards to enhance the computer system’s functionality.
- Memory: The XT motherboard supported a maximum of 640 KB of RAM using 16-pin DIP (Dual In-Line Package) memory chips installed in the memory slots.
- BIOS: This motherboard had utilized a Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) chip that controlled the initialization process during startup and provided low-level interaction instructions between the operating system and hardware.
- Connectors and Peripheral Supports: Additionally, the XT motherboard also contained various connectors for peripheral devices, such as serial ports, parallel ports, keyboard connectors, and floppy disk drive interfaces. These allowed users to connect external devices such as keyboards, printers, and storage drives to the system.
Advanced Technology (AT) motherboard
In 1984, IBM introduced advanced technology (AT) motherboard as an advancement over its predecessor, the XT motherboard. It was widely used at that time. It had a standardized form factor and connectivity of various components.
- Form Factor: The form factor of AT motherboard was approximately 12 * 13.8 inches (305 * 350 mm), larger than the XT motherboard. This larger size was essential to accommodate the components and connectors available at that time.
- Processor Support: It accommodated a 16-bit Intel 80286 processor socket, which supported faster processing and advanced memory management compared to XT systems.
- Memory: AT motherboard typically used 30-pin SIMM (Single In-Line Memory Module) memory slots for the installation of RAM.
- Expansion Slots: The IBM AT motherboard used 16-bit ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) expansion slots, which were an upgrade from the 8-bit slots used in XT motherboards. These 16-bit slots allowed the installation of peripheral devices such as:
- Sound cards
- Network cards
- Additional controllers such as graphics cards, or other interface cards.
- BIOS: This utilized firmware that controlled the initialization process during startup and provided basic input/output functions.
- Keyboard: This motherboard had unique 5-pin DIN connector for keyboards, later replaced by the PS/2 standard in newer PCs.
- Power Supply: It had two-piece power supply connector.
Standard ATX Motherboards
In 1995, Intel introduced ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) motherboard that is an enhanced version of AT motherboard. This motherboard revolutionized the industry with its improved design, expandability, and ease to use. It is the most common type of motherboards found in the desktop computers.
- Form Factor: The ATX motherboard is 12 x 9.6 inches (305 x 244 mm) in size and has COM port, LPT port, PS/2, and USB mounted directly on the motherboard. This is the most common motherboard type in desktop computers.
- Memory: ATX motherboards included multiple RAM slots that allow us to increase memory capacity and faster data access. They also featured multiple SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) ports for connecting storage drives.
- BIOS Features: The ATX motherboard included advanced BIOS chip that continuously checks the CPU temperature, voltages, cooling fans RPM, etc. If the processor over heats, the PC shuts down automatically.
- Power Supply: Power supply was positioned at the top of the previous designed motherboard, while ATX motherboards placed the power supply at the back of the case. This arrangement improved cooling and cable management.
- Integrated Ports: ATX motherboards has a inbuilt I/O (Input/Output) shield on the back panel. This shield includes ports for USB, audio, Ethernet, and other peripheral devices, simplifying the installation process.
- Expansion Slots: They typically introduced several expansion slots, including PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slots for graphics cards and other high-speed peripheral devices.
- Power Connectors: An ATX power supply has a variety of power connectors such as
- 24-pin P1 connector (main motherboard power connector used today)
- 4-pin 12-V connector
- 8-pin 12-V connector
- 4-pin Molex connector
- SATA power connector, etc.
- Common Usage:
- Business PCs
- Workstations
- Gaming system
Micro ATX Motherboards
In December 1997, Intel first introduced micro ATX motherboard, that is a smaller version of the ATX motherboard. It is designed to fit into smaller computer cases or ATX cases.
- Form Factor: Micro ATX motherboard is a 9.6 x 9.6 inches (244 x 244 mm), that makes it more compact than standard ATX motherboard. It is suitable for smaller computer cases where space is a constraint.
- Expansion Slots: Micro ATX motherboards are designed with fewer expansion slots compared to standard ATX motherboards.
- Memory: They contain multiple RAM slots to increase the memory capacity so that users can perform multitasking smoothly.
- Storage: In terms of storage, they usually provide several SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) ports for connecting hard drives and SSDs.
- Connectivity and Ports: Micro ATX come with various connectivity, including
- USB ports for peripherals.
- Audio jacks for speakers and microphones.
- Ethernet port for networking.
- Video output ports (HDMI, VGA, or DisplayPort depending on model).
- While, the number of ports may vary depending on the specific model. They generally provide ample options for connecting peripherals and external devices.
- Power Supply: A micro ATX power supply uses a 24-pin P1 connector and is not likely to have as many extra wires and connectors as compared to on an ATX power supply.
- Common Usage:
- Home PCs
- Office Desktops
Mini ITX Motherboards
In November 2001, VIA Technologies first introduced mini ATX motherboard, that is a smaller version of the micro ATX motherboard. Intel later popularized it.
- Form Factor: This motherboard is a merely 6.7 x 6.7 inches (170 x 170 mm), that makes it significantly smaller than Micro ATX and ATX. This compact size enables to design of an ultra-small PCs.
- Memory: Mini ITX motherboard has two RAM slots for a maximum memory capacity of 32 GB or more.
- Storage: It includes multiple SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) ports for connecting hard drives and SSDs mounted on mini ITX motherboard.
- Expansion Slots: It usually only one PCIe slot due to compact size.
- Connectivity and Ports: This motherboard also contains several connectivity options, including USB ports, audio jacks, ethernet ports, and video outputs.
- Common Usage:
- Compact or Home Theater PCs
Mini STX Motherboard
In 2015, Intel introduced a Mini STX (Mini Socket Technology eXtended) motherboard. The unique features of mini STX motherboard are:
- Form Factor: The Mini STX motherboard is in rectangular shape, having a dimension of 5.8 * 5.5 inches (147 mm * 147 mm). Due to its compact size, it is significantly smaller as compared to Micro ATX, and even Mini ITX motherboards.
- Processor Support: This motherboard has a unique Mini STX socket to support powerful processors, such as Intel Core i7 and i5 CPUs. This feature makes it suitable for tasks such as gaming, multimedia editing, and office productivity.
- Memory: Mini STX motherboard contains SO-DIMM memory slots for DDR3 orDDR4 RAM modules. It supports the latest memory technology for multitasking and performance.
- Storage: It also support SSDs via SATA or M.2 interface, which provides high-speed data transfer rates and ample storage capacity.
- Connectivity and Ports: Mini-STX provides many connectivity, such as USB ports, ethernet ports for networking, audio jack, and HDMI port for video.
- Expansion Slots: It usually limited to half-height PCIe expansion slots to add dedicated graphics cards, sound cards, or other expansion cards.
eXtended ATX Motherboard
An eXtended ATX motherboard is a larger variant of the standard ATX motherboard, designed for high-performance desktops and workstations.
- Form Factor: This motherboard has typically dimensions 344 millimeters by 330 millimeters (dimensions will differ with different manufacturers).
- CPU Support: An eXtended ATX motherboard supports a single or twin CPU configuration.
- Memory: It provides up to eight RAM slots, allowing for higher memory capacity.
- Expansion Slots: In addition, it has a higher number of PCIe (where e is for Express) and PCI slots. These slots may be used to add PCI cards for a wide range of applications such as gaming, video editing software, etc.
- Power Delivery System: The eXtended ATX motherboards incorporate robust power delivery systems with multiple power phases, high-quality capacitors, and voltage regulation modules. It supply the stable power to the CPU and other components that reduces the risk of system instability and improve overall performance.
- This motherboard provides additional space and features to accommodate more expansion slots, connectors, and components.
Nano-ITX Motherboard
The Nano-ITX motherboard is a small sized motherboard developed by VIA Technologies in 2003. It is designed for compact and low-power devices such as set-top boxes, smart TVs, car PCs, and embedded systems.
- Form Factor: The Nano-ITX comes in size 120 mm × 120 mm, especially designed for compact embedded and low-power computing systems. It is smaller than Mini-ITX but larger than Pico-ITX.
- Processor (CPU): This supports low-power CPUs such as VIA C3, VIA Eden, or embedded Intel/AMD processors. It often comes with the CPU soldered directly to the board for energy efficiency.
- Memory: The Nano-ITX motherboards usually support one SO-DIMM slot to install up to 4 GB or 8 GB DDR2/DDR3 memory module. It may vary on the model.
- Storage: They include SATA connectors or mSATA/IDE interfaces for SSDs or HDDs. Some models feature onboard flash storage for embedded applications.
- Expansion Slots: This has limited expansion options due to compact size. However, it may include a Mini PCIe slot for Wi-Fi or expansion modules.
- Power Supply: The Nano-ITX uses DC power input (often 12V) or external adapter. It is optimized for low power consumption and fanless operation for silent and efficient performance.
Pico-ITX Motherboard
The Pico-ITX motherboard is an even smaller motherboard standard introduced by VIA Technologies in 2007. This is designed for ultra-compact embedded systems and IoT devices where space and power efficiency are important.
- Form Factor: The Pico-ITX motherboard comes in size 100 mm × 72 mm. It is one of the smallest commercially available x86 motherboard formats.
- Processor: It uses ultra-low-power processors like VIA Eden, Intel Atom, or ARM-based CPUs.
- Memory: The Pico-ITX system typically supports one SO-DIMM slot or onboard LPDDR memory. Its maximum capacity can be usually 2 GB to 8 GB, depending on model and CPU.
- Storage: It offers SATA, microSD, or onboard eMMC storage. Some versions support mSATA or NVMe through adapters.
- Expansion Slots: The Pico-ITX system may include headers or connectors for USB, GPIO, HDMI, or Ethernet. It often requires I/O daughter boards to provide additional connectivity options.
- Power Supply: This is powered through DC input (usually 12V or 5V), which is extremely low power consumption. It is ideal for IoT and battery-powered devices.
Thin Mini-ITX Motherboard
The Thin Mini-ITX motherboard is a slimmed-down version of the standard Mini-ITX, developed by Intel in 2011. It is designed specifically for ultra-thin desktops and All-in-One (AIO) systems.
- Form Factor: The Thin Mini-ITX motherboard has the same dimensions as the Mini-ITX (170 mm × 170 mm) but a reduced height (less than 25 mm), allowing it to fit into slim enclosures.
- Processor: It supports Intel or AMD desktop and mobile processors, depending on socket type.
- Memory: This motherboard usually supports two SO-DIMM slots that are compatible with DDR3 or DDR4 laptop memory, with a maximum capacity of 32 GB or more.
- Storage: This motherboard provides SATA connectors for SSDs or HDDs and may include M.2 slots for NVMe SSDs.
- Expansion Slots: Thin Mini-ITX system includes one PCIe x4 or x1 slot (low-profile). It also includes additional headers for USB, HDMI, audio, and Ethernet.
- Power Supply: This board uses external power adapters (12V–19V DC) for energy efficient operation.
Conclusion
Today, most modern companies and manufacturers commonly use ATX and Micro-ATX motherboards in their desktop computers, office systems, and workstation because they provide the best combination of compatibility, performance, cost-efficiency, and expandability.
In this tutorial, we have discussed what is motherboard in a computer and its various types. Hope that you will have understood the basic points of computer motherboard and enjoyed this tutorial. In the next, we will get the complete knowledge of components of motherboard and their functions of a computer system.
Thanks for reading!!!